In today’s digital age, where data breaches and cyber threats are on the rise, ensuring the data privacy and security of sensitive information is critical for professional recruiters and search consultants. These professionals handle vast amounts of confidential data, including personal information, employment histories, and proprietary company data, making them prime targets for cyber attacks.
To maintain trust with clients and candidates and comply with stringent data privacy regulations, recruiters must adopt comprehensive strategies to safeguard data privacy and security effectively. And you’re in luck, because we’re going to explore the challenges faced by recruiters in protecting sensitive data and provide an in-depth analysis of best practices and strategies for mitigating risks and ensuring compliance.
Challenges in Data Privacy and Security for Recruiters
Professional recruiters and search consultants encounter various challenges in safeguarding data privacy and security. Before you can overcome these challenges, you must know exactly what they are. Unfortunately, data privacy is one of the areas of your business that is easily to overlook. However, it’s also one of the areas of your business that you should absolutely NOT overlook. So let us explore what those challenges are in today’s job market.
Data Sensitivity
Recruiters handle highly sensitive information on a daily basis, ranging from personal details to professional qualifications. Resumes, in particular, contain a wealth of personal data, including names, addresses, phone numbers, and educational backgrounds. The mishandling of this data can have severe consequences, leading to reputational damage and legal liabilities.
One of the primary challenges recruiters face is ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of this data throughout the recruitment process. From the initial collection of resumes to the final placement of candidates, recruiters must adopt stringent measures to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access, leakage, or misuse. Failure to do so not only erodes trust with clients and candidates but also exposes the organization to the risk of regulatory penalties and lawsuits.
Cyber Threats
The recruitment industry has become a lucrative target for cyber criminals seeking to exploit vulnerabilities in recruiters’ systems and processes. Phishing attacks, in particular, have emerged as a significant threat, with hackers using deceptive emails or messages to trick recruiters into disclosing sensitive information or installing malware on their systems. These attacks can have devastating consequences, ranging from data breaches to financial losses and reputational damage.
Malware infections and ransomware attacks are also prevalent in the recruitment sector, with cyber criminals exploiting weaknesses in recruiters’ IT infrastructure to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data or disrupt operations. The proliferation of remote work arrangements and reliance on cloud-based systems has further exacerbated the risk of cyber threats, as recruiters may not have adequate security measures in place to protect their data from external attacks.
Regulatory Compliance
Navigating the complex web of data privacy regulations is another significant challenge for recruiters and search consultants. In Europe, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) imposes strict requirements on the collection, processing, and storage of personal data, with hefty fines for non-compliance. Similarly, in the United States, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) grants consumers rights over their personal information and imposes obligations on businesses to protect their privacy.
Complying with these regulations requires recruiters to implement robust data protection measures, such as obtaining consent from candidates before collecting their personal information, implementing data minimization practices to limit the collection of unnecessary data, and ensuring the security of data throughout its lifecycle. Failure to adhere to these regulations can result in severe penalties, damage to reputation, and loss of business opportunities.
Third-Party Risks
Recruiters often collaborate with third-party vendors, such as job boards, an applicant tracking system (ATS), and background check providers, to streamline their operations and access a broader pool of candidates. While these partnerships offer numerous benefits, they also introduce additional risks, particularly concerning data privacy and security.
Sharing data with external parties increases the risk of data breaches, as recruiters may have limited control over how their data is handled or stored by third-party vendors. Moreover, not all vendors may adhere to the same rigorous standards of data protection, posing a potential risk to the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive information.
To mitigate these risks, recruiters must conduct thorough due diligence on third-party vendors, assessing their data security practices, compliance with relevant regulations, and track record of protecting sensitive information. Establishing clear contractual agreements outlining each party’s responsibilities for data protection is also essential to ensure accountability and mitigate potential liabilities.
Best Practices for Data Privacy and Security
As mentioned above, recruiters handle vast amounts of sensitive data, including personal information, employment histories, and proprietary company data. To address the challenges and mitigate risks associated with handling this data, recruiters should adopt a comprehensive set of best practices. With that in mind, we’ve created a list of strategies for recruiters to safeguard data privacy and security.
Implement Strong Access Controls: One of the fundamental steps in safeguarding data privacy and security is to restrict access to sensitive information to authorized personnel only. Implementing strong access controls ensures that only individuals with a legitimate need to access the data can do so. This can be achieved through user authentication mechanisms such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), which requires users to provide multiple forms of verification before gaining access to sensitive data.
Encrypt Data: Encrypting sensitive data is essential for protecting it from unauthorized access or interception. By encrypting data both in transit and at rest using robust encryption algorithms, recruiters can ensure that even if data is intercepted or stolen, it remains unreadable without the decryption key. This provides an additional layer of security, particularly when transmitting data over insecure networks or storing it on vulnerable systems.
Regular Security Audits and Assessments: Conducting regular security audits and assessments is crucial for identifying vulnerabilities in systems and processes. By systematically evaluating the effectiveness of existing security measures, recruiters can identify weaknesses and address them promptly to mitigate the risk of potential breaches. This proactive approach to security helps ensure that recruitment systems and processes remain resilient to evolving cyber threats.
Employee Training and Awareness: Employees are often the first line of defense against cyber threats, making employee training and awareness essential components of any data privacy and security strategy. Recruiters should provide comprehensive training to employees on data privacy best practices and raise awareness about the importance of safeguarding sensitive information. This includes educating staff about common cyber threats such as phishing and social engineering attacks, and providing guidance on how to recognize and report suspicious activities.
Data Minimization: Adopting a principle of data minimization is critical for reducing the risk of data exposure and misuse. Recruiters should only collect and retain the information necessary for legitimate business purposes, minimizing the amount of sensitive data stored within their systems. In addition, recruiters should establish protocols for securely disposing of obsolete or redundant data to further reduce the risk of exposure.
Secure Data Transmission: When transmitting sensitive data between parties, recruiters should use secure communication channels to prevent unauthorized access or interception. This includes using virtual private networks (VPNs) or secure file transfer protocols (SFTP) to encrypt data in transit and protect it from prying eyes. Avoiding the use of unencrypted email or messaging platforms for transmitting sensitive information is also essential for maintaining data security.
Vendor Due Diligence: Many recruiters rely on third-party vendors to streamline their operations and access additional resources. However, sharing data with external parties introduces additional risks, making vendor due diligence a critical component of data privacy and security. Recruiters should perform thorough due diligence on third-party vendors before engaging their services, ensuring that they have robust data security measures in place and comply with relevant regulations. Establishing clear contractual agreements outlining each party’s responsibilities for data protection helps ensure accountability and mitigate potential liabilities.
Incident Response Plan: Despite best efforts to prevent data breaches, incidents may still occur. Having an incident response plan in place is essential for minimizing the impact of security incidents and mitigating further damage. Recruiters should develop and regularly update an incident response plan outlining procedures to follow in the event of a data breach or security incident. This includes ensuring that all staff are familiar with their roles and responsibilities during such scenarios and establishing clear communication protocols for notifying stakeholders and managing public relations.
Monitor and Audit User Activity: Implementing logging and monitoring tools to track user activity within recruitment systems helps detect any unauthorized access or suspicious behavior. By regularly reviewing audit logs, recruiters can identify potential security incidents or policy violations and take appropriate action to address them. This proactive approach to monitoring user activity helps maintain the integrity of recruitment systems and ensures compliance with data privacy regulations.
Stay Informed About Regulatory Changes: Staying abreast of developments in data privacy regulations is essential for ensuring compliance with relevant laws and guidelines. Recruiters should establish processes for monitoring regulatory changes and adapting practices accordingly. This includes regularly reviewing and updating data privacy policies and procedures to reflect changes in the legal landscape and implementing necessary measures to remain in compliance.
Expanding on Best Practices for Data Privacy and Security
But wait, there’s more! Building upon the foundational best practices, we’re going to dive further into the intricacies of implementing robust measures to fortify data protection and mitigate risks effectively. Expanding on key areas such as access controls, data encryption, employee training, vendor due diligence, and incident response planning is essential to establish a comprehensive framework for ensuring data integrity and confidentiality as a professional recruiter or search consultant.
Implementing Strong Access Controls
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is pivotal in governing access to sensitive data within an organization. By assigning access rights based on users’ roles and responsibilities, RBAC ensures that employees only have access to the data essential for their job functions. This granular approach minimizes the risk of unauthorized access and limits exposure to sensitive information.
In addition, Privileged Access Management (PAM) solutions play a crucial role in managing and monitoring privileged accounts, such as administrative accounts, which hold elevated access rights. By enforcing strict controls and monitoring privileged access activities, organizations can mitigate the risk of insider threats and unauthorized access attempts. Implementing PAM solutions also facilitates accountability and traceability, enabling organizations to track and audit privileged access activities effectively.
Encrypting Data
While implementing encryption is fundamental to data security, robust key management practices are equally essential to ensure the effectiveness of encryption mechanisms. Implementing robust key management practices involves securely generating, storing, and distributing encryption keys, as well as regularly rotating encryption keys to mitigate the risk of key compromise. By implementing comprehensive key management practices, organizations can maintain the confidentiality and integrity of encrypted data throughout its lifecycle.
Furthermore, data masking techniques play a vital role in anonymizing sensitive data in non-production environments, such as development and testing environments. By masking sensitive information, organizations can prevent exposure of confidential data to unauthorized users while ensuring that realistic data sets are available for testing and development purposes. Data masking techniques such as tokenization and pseudonymization enable organizations to achieve a balance between data utility and privacy protection.
Employee Training and Awareness
In the battle against cyber threats, employees are often the first line of defense. Conducting regular phishing simulations is instrumental in assessing employees’ susceptibility to phishing attacks and enhancing awareness about phishing tactics. By simulating real-world phishing scenarios and providing targeted training based on simulation results, organizations can empower employees to identify and report phishing attempts effectively.
Moreover, raising awareness about common social engineering tactics used by cyber criminals, such as pretexting and baiting, is essential for building a resilient workforce. By educating employees about social engineering tactics and providing guidance on verifying the authenticity of requests for sensitive information, organizations can mitigate the risk of falling victim to social engineering attacks. Employee training and awareness initiatives play a pivotal role in fostering a culture of security consciousness and empowering employees to play an active role in safeguarding data privacy and security.
Vendor Due Diligence
In an era of increasing outsourcing and collaboration with third-party vendors, conducting thorough security assessments is essential to assess vendors’ data security practices and compliance with industry standards. By requiring third-party vendors to undergo security assessments, organizations can evaluate vendors’ vulnerability management processes, incident response capabilities, and data encryption practices. This enables organizations to make informed decisions about engaging third-party vendors and ensures that vendors adhere to stringent security standards.
Moreover, incorporating data protection clauses in contracts with third-party vendors is essential to outline vendors’ responsibilities for safeguarding data and reporting security incidents. By specifying requirements for data encryption, access controls, and data breach notification procedures, organizations can establish clear expectations and accountability mechanisms for third-party vendors. Contractual obligations play a vital role in ensuring that third-party vendors align with organizations’ data privacy and security requirements and uphold the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive data.
Incident Response Plan
Preparing for potential security incidents is paramount in mitigating the impact of data breaches and ensuring an effective response. Conducting tabletop exercises to simulate various security incidents, such as data breaches or malware infections, enables organizations to test the effectiveness of their incident response plan and identify gaps in procedures. By simulating realistic scenarios and evaluating the organization’s response capabilities, organizations can refine their incident response plan and improve response readiness.
In addition, establishing clear communication protocols for notifying stakeholders in the event of a data breach is essential for managing the aftermath of security incidents effectively. By designating spokespersons to liaise with the media and manage public relations during a security incident, organizations can maintain transparency and trust with stakeholders. Communication protocols play a pivotal role in facilitating timely and transparent communication with employees, clients, regulatory authorities, and the public, thereby minimizing the reputational damage and legal ramifications associated with data breaches.
Professional recruiters and search consultants face significant challenges in safeguarding data privacy and security due to the sensitive nature of the information they handle and the evolving threat landscape. As a result, it’s essential for recruiters to remain vigilant and proactive in addressing emerging cyber threats and regulatory requirements to maintain trust with clients and candidates and uphold the integrity of their operations in the recruitment industry.
Data Privacy and Top Echelon Software
Top Echelon Software offers a comprehensive suite of tools and solutions designed to assist professional recruiters and search consultants in navigating the challenges of data privacy and security effectively. With a focus on empowering recruiters to streamline their operations while maintaining the highest standards of data protection, Top Echelon Software provides several key features and functionalities to enhance data privacy and security, including what we have listed below.
Robust Access Controls: Top Echelon Software enables recruiters to implement strong access controls, allowing them to restrict access to sensitive data to authorized personnel only. By utilizing role-based access control (RBAC) mechanisms, recruiters can ensure that employees only have access to the data necessary for their job functions, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access.
Secure Data Encryption: Top Echelon Software employs robust encryption techniques to safeguard sensitive data both in transit and at rest. By encrypting data using industry-standard encryption algorithms, such as AES, recruiters can ensure that even if data is intercepted or stolen, it remains unreadable without the decryption key.
Compliance Management: Top Echelon Software helps recruiters stay compliant with data privacy regulations by providing tools and resources to monitor and manage regulatory compliance. With features such as compliance reporting and audit trails, recruiters can demonstrate adherence to regulations such as GDPR and CCPA, minimizing the risk of regulatory penalties.
Vendor Due Diligence: Top Echelon Software assists recruiters in conducting due diligence on third-party vendors to ensure they meet stringent data security standards. By vetting vendors’ data security practices and compliance with relevant regulations, recruiters can minimize the risk of data breaches associated with third-party partnerships.
Overall, Top Echelon Software plays a vital role in helping professional recruiters and search consultants enhance data privacy and security, enabling them to focus on their core business objectives with confidence.
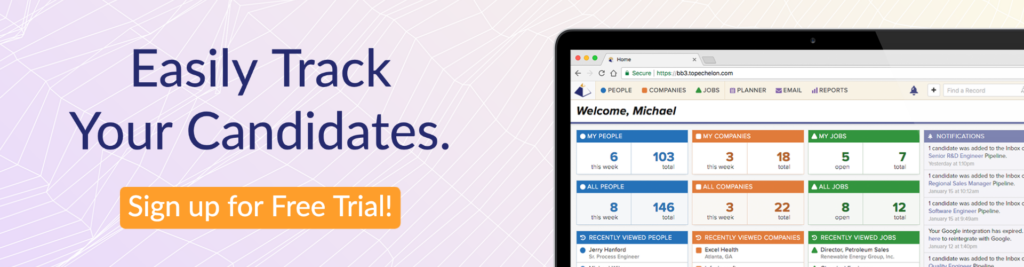
And you can try Top Echelon for yourself! That’s because you can get free recruitment software as part of your trial.
Not only that, but you can also request a recruiting software demo and see for yourself how Top Echelon can help you save time while making more money.
We also encourage you to check out Top Echelon’s recruitment software pricing page for more information about the affordability of our ATS.