The gig economy, characterized by short-term contracts and freelance work, has seen explosive growth in recent years. It offers unparalleled flexibility and opportunities for both workers and businesses. However, this burgeoning sector also presents numerous challenges for professional recruiters and search consultants.
The transient and decentralized nature of gig work creates unique hurdles that require innovative solutions. In this article from Top Echelon Recruiting Software, we will address the myriad challenges posed by the gig economy and provide detailed strategies that recruitment professionals can implement to navigate these issues effectively, ensuring their clients’ success in this ever-evolving job market.
Challenges in the Gig Economy
There are numerous challenges for agency recruiters and search consultants in terms of the gig economy. They include a talent shortage and high turnover rates, remote work and communication barriers, compliance and legal concerns, skill verification and credentialing, cultural fit and company values, compensation and benefits, talent scalability, data privacy and security, client education and expectation management, and technology and automation.
We shall explore each of these challenges. And as a bonus, we’ll have a solution for each challenge! (Which . . . is exactly what the title of this blog post promised.)
Talent Shortage and High Turnover Rates
One of the most pressing challenges in the gig economy is the scarcity of highly skilled and reliable talent. Gig workers often juggle multiple clients, making it difficult for recruiters to find individuals committed to long-term projects. This transience results in high turnover rates, necessitating constant recruitment efforts and creating instability for businesses relying on gig workers.
Solution:
Develop relationships with gig workers: Building strong networks with freelancers and contractors can ensure a pool of trusted talent is readily available when clients require it. Personal relationships can lead to greater loyalty and commitment from gig workers.
Engage in continuous talent mapping: Maintaining up-to-date profiles of potential gig workers and regularly communicating with them helps recruiters stay informed about their availability and skills. This proactive approach can significantly reduce the time spent searching for new candidates and improve the quality of hires.
Remote Work and Communication Barriers
The gig economy relies heavily on remote work arrangements, which can lead to significant communication challenges. Recruiters may find it difficult to assess a candidate’s soft skills, such as teamwork and communication, through virtual interactions. This limitation can result in mismatches between client expectations and worker abilities, impacting project outcomes.
Solution:
Implement comprehensive assessments: Develop tailored assessments and interview questions that gauge remote work skills, communication abilities, and adaptability. These assessments should be designed to mimic real-life scenarios that gig workers might encounter.
Leverage video interviews: Use video interviews to simulate face-to-face interactions, allowing recruiters to assess non-verbal communication cues. Additionally, incorporating situational judgment tests can provide deeper insights into a candidate’s problem-solving and decision-making abilities in a remote setting.
Compliance and Legal Concerns
Navigating the gig economy often involves complex labor laws and regulations. Misclassification of workers as independent contractors instead of employees can lead to legal consequences, including fines and back taxes. Ensuring compliance is critical to avoid costly mistakes and legal liabilities.
Solution:
Stay informed about labor laws: Regularly educating oneself about the latest changes in labor laws and regulations related to gig workers is essential. Attending workshops, webinars, and industry conferences can help recruiters stay updated.
Work with legal experts: Partnering with legal professionals who specialize in labor law can ensure that gig workers are properly classified. Legal experts can provide guidance on drafting contracts and agreements that comply with relevant regulations, reducing the risk of misclassification.
Skill Verification and Credentialing
Gig workers may lack traditional resumes or educational backgrounds, making it challenging for recruiters to verify their skills and credentials accurately. This can hinder the selection of the most qualified candidates for client projects, impacting the quality of deliverables.
Solution:
Develop skills assessments: Creating customized skills tests and assessments that directly measure the competencies required for specific roles or projects can provide objective data on a candidate’s abilities. These tests should be designed to evaluate both technical and soft skills.
Encourage portfolio submissions: Requesting gig workers to provide portfolios or work samples showcasing their abilities and past achievements can offer valuable insights into their expertise and suitability for the job. Portfolios can demonstrate practical experience and the quality of previous work.
Cultural Fit and Company Values
Ensuring that gig workers align with a client’s company culture and values is challenging. A misalignment in these areas can lead to dissatisfaction and potential conflicts, affecting team dynamics and project success.
Solution:
Conduct culture interviews: Including culture-fit interviews in the selection process can help assess a candidate’s alignment with the client’s organizational values and work culture. These interviews should focus on understanding the candidate’s work preferences, values, and motivations.
Provide cultural orientation: Offering resources and onboarding materials to help gig workers understand and integrate into the client’s company culture can facilitate smoother transitions. Providing training sessions or mentorship programs can also aid in acclimatizing gig workers to the company’s environment.
Compensation and Benefits
Gig workers often lack traditional employee benefits like health insurance, retirement plans, and paid time off. This can lead to challenges in negotiating compensation packages that attract and retain top talent, as many gig workers prioritize these benefits.
Solution:
Offer competitive pay rates: Staying informed about industry compensation benchmarks and adjusting pay rates accordingly can help attract skilled gig workers. Conducting market research to understand competitive rates can ensure that compensation packages are appealing.
Explore benefits packages: Considering alternative benefits such as flexible schedules, training opportunities, or performance-based bonuses can make gig work more appealing. Offering access to resources like health and wellness programs or financial planning services can also enhance job satisfaction and loyalty.
Talent Scalability
Client organizations may require an influx of gig workers during peak seasons or for specific projects. Scaling up or down rapidly can be challenging for recruiters who need to ensure a seamless workflow and maintain project continuity.
Solution:
Maintain a talent pipeline: Continuously engaging with potential gig workers and keeping track of their availability and skills can enable quick scaling when needed. Building a database of pre-vetted candidates allows recruiters to respond swiftly to client demands.
Partner with talent agencies: Collaborating with talent agencies specializing in the gig economy can provide access to a broader pool of available workers. These agencies often have extensive networks and can facilitate rapid scaling by matching clients with suitable candidates.
Data Privacy and Security
As remote work becomes more prevalent, data privacy and security concerns grow. Recruiters must ensure that gig workers handle sensitive client information responsibly and securely, safeguarding against potential breaches and data leaks.
Solution:
Conduct background checks: Verifying the security protocols and practices of gig workers can ensure they meet the client’s data privacy requirements. Background checks should include assessing the candidate’s history of handling sensitive information.
Implement NDAs and contracts: Including robust non-disclosure agreements and contractual clauses addressing data security in gig worker agreements can protect client information. Clearly outlining expectations and responsibilities regarding data handling can mitigate risks.
Client Education and Expectation Management
Clients may not fully understand the intricacies of the gig economy and its challenges. It falls upon recruiters to educate clients and manage their expectations regarding the availability, commitment, and productivity of gig workers.
Solution:
Offer client workshops: Organizing workshops or seminars to educate clients about the gig economy and its benefits and limitations can foster better understanding. Providing case studies and success stories can illustrate how to effectively leverage gig workers.
Set clear expectations: Communicating realistic timelines, deliverables, and work arrangements to clients can avoid misunderstandings. Establishing clear terms and conditions in contracts can ensure that both parties have aligned expectations.
Technology and Automation
As the gig economy evolves, recruiters need to adapt to new technology and automation tools for sourcing, onboarding, and managing gig workers efficiently. Staying abreast of technological advancements is crucial for maintaining competitiveness and streamlining processes.
Solution:
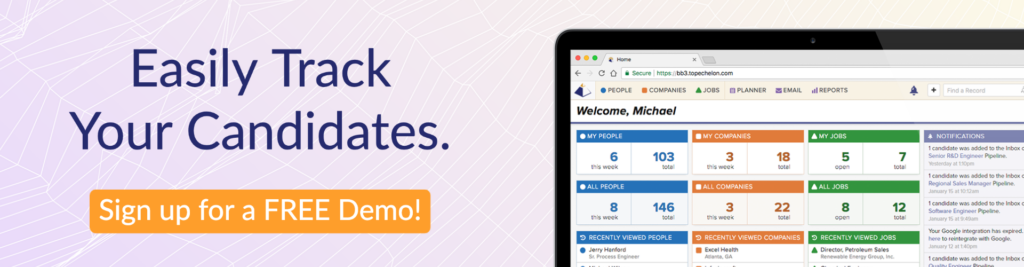
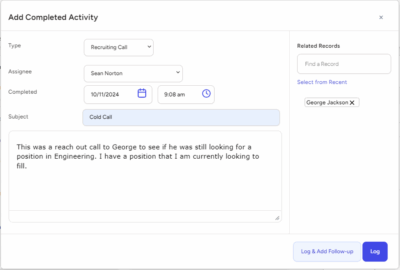
Invest in recruitment software: Utilizing applicant tracking systems (ATS), customer relationship management (CRM) tools, and other technologies can streamline the recruitment process. These tools can automate tasks such as job postings, application tracking, and candidate communication.
Leverage AI and automation: Implementing AI-driven algorithms to match gig workers with suitable projects can enhance efficiency. Automation can also handle routine tasks such as background checks and document verification, freeing up recruiters to focus on more strategic activities.
Gig Economy: Final Word for Recruiters
The gig economy presents a host of challenges for professional recruiters and search consultants, from talent shortages and compliance issues to communication barriers and cultural fit concerns. However, by embracing innovative solutions and adapting to the changing job landscape, recruiters can help their clients navigate these challenges effectively.
To thrive in the gig economy, recruiters should continually educate themselves about industry trends and labor laws, develop customized assessments and interview processes, and cultivate strong relationships with gig workers. By doing so, they can bridge the gap between clients and the gig workforce, ensuring successful and mutually beneficial partnerships in this dynamic employment landscape.
The future of work is increasingly leaning towards flexibility and freelance engagements. As such, recruiters who can adeptly manage the nuances of the gig economy will be well-positioned to provide exceptional value to their clients. With the right strategies in place, the gig economy can be a win-win for both workers seeking flexibility and businesses aiming for agility and innovation.